Paco2 Normal Range
The shape of the oxygenhemoglobin curve starts to flatten at SpO2 of 90 for this reason PaO2 is a poor indicator of oxygen content. This is known as.
Normal bleeding time.

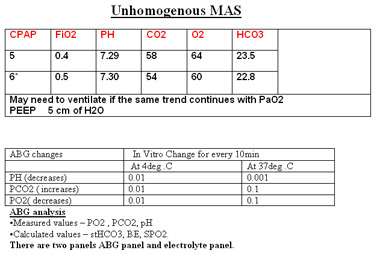
Paco2 normal range. A patient has the following arterial blood gas results. On the flip side if the pH was not normal but the HCO3 was normal it would be uncompensated. PAO2 FiO2 760 PH2O PaCO208.
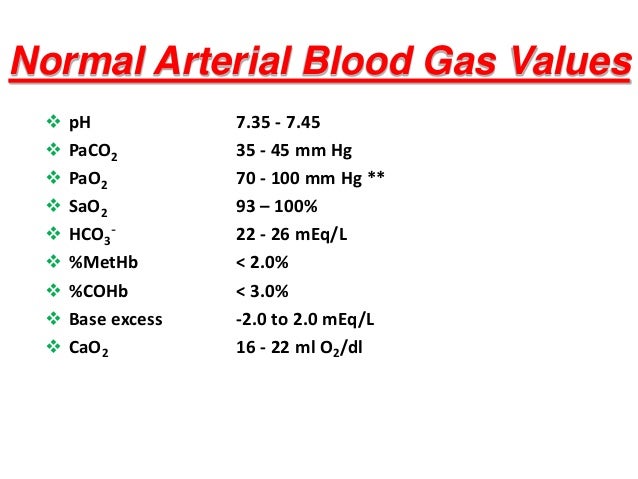
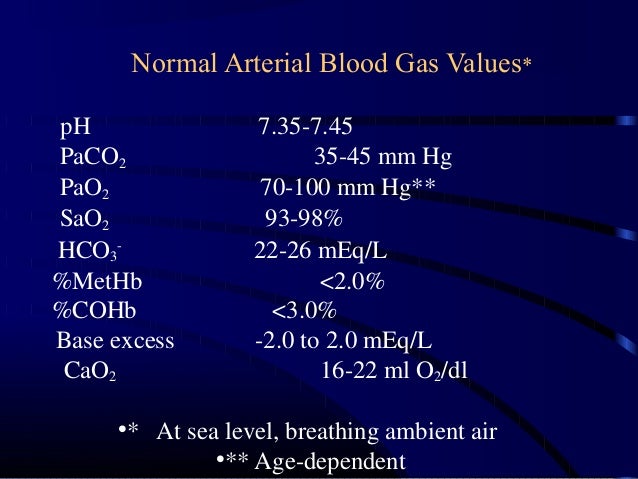
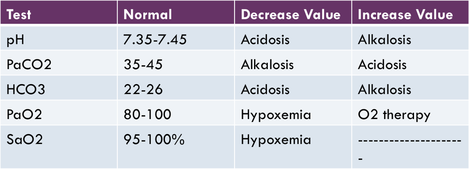
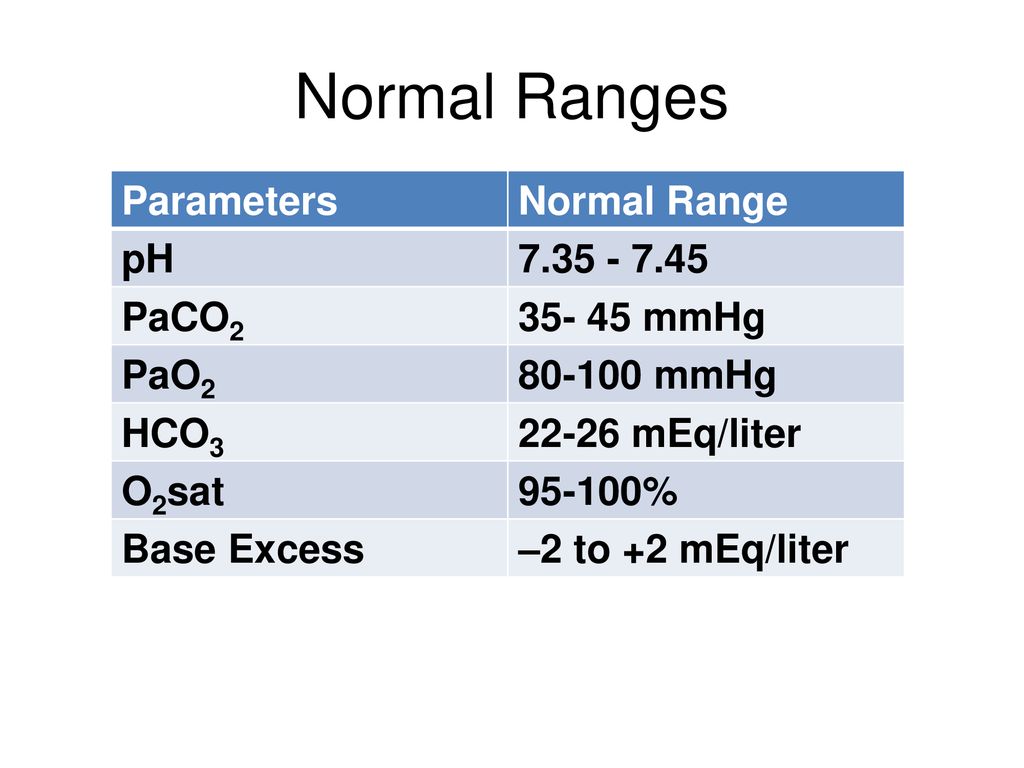
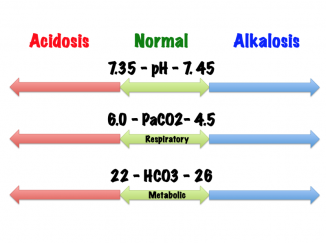
The normal range for pH is 735745. A pH of less than 70 is called acid and a pH higher than 70 is called basic alkaline. Metabolic acidosis fully compensated by the means of respiratory alkalosis.
How to Interpret an ABG. In other words a pH of 737 would be categorized as acidosis and a pH of 742 would be categorized as alkalemia. Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide PaCO2.
The pH measures hydrogen ions H in blood. If a patients pH 745 the patient is in alkalosis. 96 to 100.
PaO2 is maintained because of the preserved matching of ventilation and perfusion as alveolar walls are destroyed. Oxygen saturation O2 Sat. Values less than this may indicate hyperventilation and if blood pH is greater than 745 respiratory alkalosis.
Bicarbonate HCO3 22 to 26 milliequivalents per liter mEqliter. Longitudinal assessment of changes in. When PaCO2 and HCO3 values are high but pH is acidic then it indicates partial compensation.
Elimination of carbon dioxide. The job of the respiratory system is to keep the body constantly supplied with oxygen. A normal pH value is between 735 and 745.
However normal diffusion occurs normal A-a gradient the arterial PaO2 decreases and hypoxemia results. With exertion or distress 100-150. Oxygen saturation SaO2 95 to 100.
22 to 26 mEqL. Target 6 -8 LPM OPD 1015 ARDS Peak Flow Clinical range. PaCO2 3545 mmHg 4760 kPa PaCO2 45 mmHg 60 kPa.
The normal range of partial pressure of carbon dioxide is between 35 and 45 millimeters of mercury mmHg. If the value is higher than 45 mmHg its indicative that you have too much carbon dioxide in your blood. However the A-a gradient is an excellent indicator of gas exchange.
The respiratory system organs oversee the gas exchanges that occur between the blood and the external environment. 94-100 Show Me Nursing Programs. 3 to 7 minutes.
The PaCO2 level tells you how much carbon dioxide there is in the blood and the HCO3 level tells you how much bicarbonate is in the blood. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO2. OLeary P Boyne P Flett P et al.
Passageways that allow air to reach the lungs. Normal Results Range. Next evaluate the respiratory and metabolic components of the ABG results the PaCO2 and HCO3 respectively.
Venous Lab Values Normal Range. Normal100 mLcmH2O lung 50. However in large.
The FiO2 used should always be specified. May be lower if drug OD hypothermic deep sedation. All compensatory responses work to restore the pH to the normal range 735 745.
Normal values for humans are in the range 3545 mmHg. Oxygen therapy can correct the hypoxemia in this instance because the inspired air increases the PAO2 back to normal levels. Partial Pressure of Oxygen PaO2.
If pH is abnormal and if the value of either PaCO2 or HCO3 is abnormal it indicates that the system is uncompensated. 85 to 100 mm Hg. PaCO2 is maintained because the ventilatory response to CO2 is not usually impaired.
The decreased atmospheric pressure at altitude causes a decreased PAO2. 35 to 45 mm Hg. In general patients with relatively pure emphysema maintain blood gases in or near the normal range until very late in their course.
Blood pH 750 PaCO2 49 and HCO3 30 mEqL. Establishing a normal range for D-dimer levels through pregnancy to aid in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. A pure metabolic acidosis low HCO3- normal PaCO2 and a low pH should elicit a compensatory decrease in PaCO2 and a pure metabolic alkalosis high HCO3- normal PaCO2 and high pH should cause a compensatory increase in PaCO2.
Normal minute ventilation is from 4-7 Lmin. The functions of the respiratory system are. A quick comparison of the patients PaO2 to the product of 500 x FiO2 is a magic trick for estimating a-A gradient that should be in the arsenal of every intensivist.
This measures the pressure of CO2 dissolved in the blood and how well carbon dioxide has the ability to move out of the body. Normal deadspace ventilation makes up 30 of that. Under 35 mmHg and you have too little.
As the pH decreases 735 it implies acidosis while if the pH increases 745 it implies alkalosis. May be higher 8-14 LPM if OPD or ARDS. A normal PaCO2 is between 35-45 miliLiters mercury and a normal HCO3 is between 22-26 miliEquivalents per liter.
The pH of blood is usually between 735 and 745. Ventilator default 60LPM Compliance v p V TPlateau-PEEP -Static compliance. Values greater than 45 mmHg may indicate hypoventilation and if blood pH is less than 735 respiratory acidosis.
Partial pressure of oxygen PaO2 75 to 100 millimeters of mercury mmHg Partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO2 35 to 45 mmHg. Carbon dioxide is dissolved in the blood as carbonic acid a weak acid. Partial pressure of CO2 PaCO2.
Respiratory compensation for metabolic alkalosis if pH. Determine the respiratory component PaCO2 Primary respiratory acidosis hypoventilation if pH. The first value a nurse should look at is the pH to determine if the patient is in the normal range above or below.
J Thromb Haemost 2004. It means that the compensatory mechanism tried but failed to bring the pH to normal. If the pH is in the normal range 735-745 use a pH of 740 as a cutoff point.
Shunt is not suspected. In the context of arterial blood gases the most common occurrence will be that of respiratory acidosis. The PaCO2 is normal and.

Normal Abg Values Uk Sodusvillage Org
Arterial Blood Gases Abg S Cardiovascular And Pulmonary

How To Interpret Arterial Blood Gas Results The Pharmaceutical Journal

Blood Gas Acid Base Analysis And Electrolyte Abnormalities Veterian Key

Arterial Blood Gas Analysis And Acid Base Balance Disorders Medcrine
Interpretation Of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis

Normal Values For Arterial Blood Gases In Pregnant And Non Pregnant Women Download Scientific Diagram
Blood Gas Analysis Ppt Download

Ems News Feature Article From Thomson Delmar Learning Nursing School Essential Nursing School Tips Nursing Mnemonics
Arterial Blood Gases Physiopedia

Nursesoutlook Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Nursesoutlook

Blood Gases Normal Lab Values Flashcards Quizlet

Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Ppt Download

Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Flashcards Quizlet

The Normal Paco2 According To Altitude And Barometric Pressure Download Table